Treatments & Procedures
Nothing looks, feels or functions like your natural tooth. Regular brushing and flossing, along with six-month check-ups from you dentist, can help you keep your teeth for a lifetime.
Sometimes your teeth may have infection or disease and will need additional care. When possible, you should always consider treatments to save your teeth. You may think, why not have a tooth pulled, especially if no one can see it, but you will know your tooth is missing and it will negatively impact your quality of life.
Don’t get a tooth pulled because you think its easier or more cost-effective. Missing teeth can cause other teeth to shift, affect your ability to properly chew and ruin your smile. Tooth extraction often is more painful than the infection itself, and replacing an extracted tooth with an artificial one requires additional dental visits that can quickly add up.
Modern endodontics offers advancements in technologies, procedures and materials, giving you many treatment options to save your natural teeth. It’s important to understand your choices and how they’ll impact both your tooth and your future dental health. It’s always best to retain your natural teeth whenever possible and endodontic treatment should be your first choice for the best health and cosmetic results. Endodontists are specialists in saving teeth. They can evaluate your condition and provide the best treatment plan to help you save your teeth for a lifetime.
Here are some tips for saving your teeth:
- When given a choice between tooth extraction and root canal treatment, always opt for a root canal. No denture, bridge or implant will look, feel and function as well as a natural tooth.
- Act immediately when you experience symptoms of swelling or pain. Most endodontists can accommodate emergency cases, even on weekends, ensuring you’ll be seen quickly.
- If your dentist recommends tooth extraction, ask whether the root canal is an option.
- If you’re told root canal is not an option, ask why and request a referral to an endodontist or use the AAE’s Find an Endodontist search tool to find a practice near you.
Root canals treatment from an endodontist is virtually painless and often leaves you with less discomfort during recovery than if you have your natural tooth extracted. Thanks to modern techniques and effective anesthesia, patients who experience root canals are six times more likely to describe it as painless than patients who have a tooth extracted! Take the time to learn more about root canal treatment and some of the common misconceptions about it and then take the first step to a pain-free, healthy mouth by visiting an endodontist near you.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
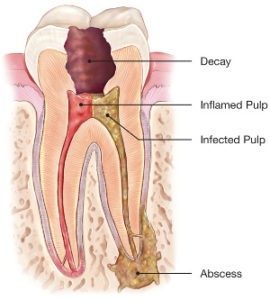 What is a Root Canal?
What is a Root Canal?
Root canal treatment is an often straightforward procedure to relieve dental pain and save your teeth. Patients typically need a root canal when there is inflammation or infection in the roots of a tooth. During root canal treatment, an endodontist who specializes in such treatment carefully removes the pulp inside the tooth, cleans, disinfects and shapes the root canals, and places a filling to seal the space.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
With proper care, you’ll keep teeth that have had root canal treatment for a lifetime but it’s possible for those teeth to heal improperly, becoming painful or diseased months or even years after treatment. If this happens to your treated teeth you have a second chance to save the tooth with retreatment. An additional procedure may be able to diminish dental pain or discomfort and promote healing. If you suspect a tooth that had a prior root canal requires retreatment, visit your dentist or endodontist for evaluation.
As with any dental or medical procedure, it’s possible your tooth won’t heal as expected after initial treatment for a variety of reasons, including:
- Narrow or curved canals were not treated during the initial procedure.
- Complicated canal anatomy went undetected in the first procedure.
- The placement of the crown or other restoration was delayed following the endodontic treatment.
- The restoration did not prevent salivary contamination to the inside of the tooth.
A new problem can also jeopardize a tooth that was successfully treated, such as:
- New decay can expose the root canal filling material to bacteria, causing a new infection in the tooth.
- A loose, cracked or broken crown or filling can expose the tooth to new infection.
- A tooth sustains a fracture. During retreatment, the endodontist will reopen your tooth and remove the filling materials that were placed in the root canals during the first procedure. The endodontist then carefully examines the tooth, looking for additional canals or new infection. The endodontist then removes any infection, cleans and shapes the canals, and places new filling materials. The opening is then sealed with a temporary filling. Once the tooth heals, a new crown or other restoration is placed on the tooth to protect it.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
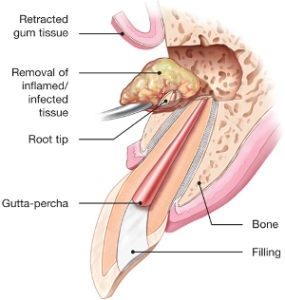 It’s possible that a nonsurgical root canal procedure won’t be enough to save your tooth and that your endodontist will recommend surgery. Endodontic surgery can be used to locate small fractures or hidden canals previously undetected on X-rays during the initial treatment. Surgery may also be needed to remove calcium deposits in root canals, or to treat damaged root surfaces or the surrounding bone of the tooth.
It’s possible that a nonsurgical root canal procedure won’t be enough to save your tooth and that your endodontist will recommend surgery. Endodontic surgery can be used to locate small fractures or hidden canals previously undetected on X-rays during the initial treatment. Surgery may also be needed to remove calcium deposits in root canals, or to treat damaged root surfaces or the surrounding bone of the tooth.
There’s no need to worry about surgery if your endodontist prescribes this additional measure. Advanced technologies like digital imaging and operating microscopes allow these procedures to be performed quickly, comfortably and successfully.
There are many surgical procedures that can be performed to save a tooth. The most common is called an apicoectomy, or root-end resection, which may be needed when inflammation or infection persists in the bony area around the end of your tooth after a root canal procedure.
Your endodontist performs this micro surgical procedure first making you comfortable by applying local anesthesia before opening the gum tissue near the tooth to see the underlying bone and to remove any inflamed or infected tissue. The very end of the root is also removed. A small filling may be placed to seal the end of the root canal and a few stitches or sutures are placed to help the tissue heal. In the next few months, the bone will heal around the end of the root. Most patients return to their normal activities the next day. Post-surgical discomfort is generally mild.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
The thought of a root canal may make you fearful or uneasy if you aren’t familiar with the procedure. There are common misconceptions that endodontic treatments such as root canals, cause pain and/or illness and should be avoided at all costs. The exact opposite is true. The pain, inconvenience and cost of avoiding endodontic treatment in favor of tooth extraction or a wait-and-see approach can be easily avoided. The longer you postpone treatment the more you risk the chance to save your tooth. Take the time to read the information on our website to find out what endodontists do to save teeth with minimal time and discomfort. Then address any remaining concerns or questions with your dentist or endodontist.
Put your mind at ease as we dispel three common myths about root canals:
Myth 1: Root canal treatment is painful.
Decades ago that may have been the case, but with modern technology and anesthetics you won’t experience any more pain than if you went to have a cavity filled. The pain from a severe toothache, often caused by damaged tissues in the tooth, can be easily remedied when an endodontist removes the damaged tissue through root canal treatment. In addition, endodontists are experts in pain management, and most cases can be treated quickly and comfortably.
Myth 2: Root canal treatment causes illness.
Information you may find on the Internet or elsewhere, claiming that if you receive a root canal treatment you’re more likely to become ill or contract a disease in the future simply isn’t true. This false claim was based on long-debunked and poorly designed research conducted nearly a century ago, long before modern medicine understood the causes of many diseases. There is no valid, scientific evidence linking root canal treatment to disease elsewhere in the body.
Myth 3: It’s better to pull a tooth than have root canal treatment.
Saving your natural teeth, if possible, is always the best option. Nothing artificial can replace the look or function of a natural tooth so it’s important to always consider root canal treatment as an option. Endodontic treatment has a high success rate and many root canal-treated teeth last a lifetime. Replacing an extracted tooth with a bridge or implant requires more time in treatment and may result in further procedures to neighboring teeth and supporting tissue.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
Root canal treatment means the end of pain, not the beginning of it. Anyone who’s ever suffered from pulp inflammation or infection knows the hurt of toothache, which only gets worse the longer it goes untreated. Even taking a sip of water can be a painful experience to someone in need of root canal treatment.
An endodontist is well aware of the painful plight of toothache, and they are experts in pain management. An endodontist makes patient comfort a priority and strives to keep procedures pain free, with advanced numbing techniques and a gentle bedside manner.
With modern techniques and anesthetics, most patients report that they are comfortable during the procedure.
For the first few days after treatment, your tooth may feel sensitive, especially if there was an infection before the procedure. This discomfort can be relieved with over-the-counter or prescription medications. Follow your endodontist’s instructions carefully.
When is it time to see an endodontist?
No one enjoys having work done on their teeth and some even delay their bi-annual cleanings out of fear or reluctance to visit the dentist. But when it comes to real tooth pain, it’s important to take care of it as soon as possible. You’ll feel better and likely save your tooth.
If you’re experiencing tooth pain, have injured your tooth, feel sensitivity to hot or cold, and/or there is swelling around the teeth, gums or your face, make an appointment with an endodontist or pay a visit to your dentist, first.
Your dentist may refer you to an endodontist — an expert at saving teeth with two or more years of specialized training above and beyond dental school.
Always keep in mind that beginning your root canal procedure means ending your tooth pain.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
Traumatic dental injuries often occur as a result of an accident or sports injury. The majority of these injuries are minor – chipped teeth. It’s less common to dislodge your tooth or have it knocked completely out but these injuries are more severe. Treatment depends on the type, location and severity of each injury. Regardless of the extent of the injury, your tooth requires immediate examination by a dentist or an endodontist. Sometimes, your neighboring teeth suffer an additional, unnoticed injury that can only be detected by a thorough dental exam.
Endodontists are dentists who specialize in treating traumatic dental injuries. With their advanced skills, techniques and technologies they often can save injured teeth. If you have a cracked or injured tooth, find an endodontist near you right away. Most endodontists offer tremendous flexibility in accommodating emergency cases, including weekends in some instances. You’ll have relief from your pain and likely save your tooth, so act as quickly as possible.
Knocked Out Teeth (Avulsed Teeth)
More than five million teeth are knocked out every year in children and adults but if this happens to you due to an injury or accident it doesn’t necessarily mean it’s lost for good. Proper emergency action can save the tooth so that it can be replanted successfully and last for years to come.
Act quickly, within 30 minutes, and visit the nearest dentist or endodontist.
Review and remember these tooth-saving steps that take you and your tooth from the time it falls out until you reach medical support:
- Pick up the tooth by the crown (the chewing surface) NOT the root.
Locate the tooth immediately; don’t leave it at the site of the accident. Handle the tooth carefully when you pick it up, and never touch the root of the tooth, only the crown (chewing surface).
- If dirty, gently rinse the tooth with water.
Use only water to gently rinse off any dirt. Do not use soap or chemicals. Don’t scrub or dry the tooth, and don’t wrap the tooth in a tissue or cloth.
- Reposition the tooth in the socket immediately, if possible.
Try to put the tooth back into its socket right away. Gently push it in with your fingers, by handling the crown, or position it above the socket and close your mouth slowly. Hold the tooth in place with your fingers or by gently biting down on it.
- Keep the tooth moist at all times.
The tooth must stay moist at all times, either in your mouth or, if it can’t be replaced in the socket, put it in milk, in your mouth next to your cheek, or in an emergency tooth preservation kit (such as Save-a-Tooth®). Don’t use regular tap water; root surface cells can’t tolerate that for extended periods of time.
- See an endodontist or dentist within 30 minutes of the injury.
Bring the tooth with you to your emergency appointment ideally. It’s best to see the doctor within 30 minutes; however, it is possible to save a tooth even if it has been outside the mouth for an hour or more
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
Whether your tooth cracks from an injury or general wear and tear, you can experience a variety of symptoms ranging from erratic pain when you chew your food to sudden pain when your tooth is exposed to very hot or cold temperatures. In many cases, the pain may come and go and your dentist may have difficulty locating the tooth causing the discomfort. If you experience these symptoms or suspect a cracked tooth, it’s best to see an endodontist as soon as possible.
Endodontists specialize in saving cracked teeth and will cater treatment to the type, location, and extent of the crack. The sooner your tooth is treated, the better the outcome. Once treated, most cracked teeth continue to function as they should, for many years of pain-free biting and chewing.
Why does a cracked tooth hurt?
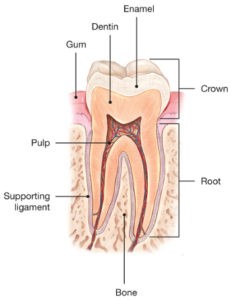 To understand why a cracked tooth hurts, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is the inner soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains the tooth’s nerves and blood vessels.
To understand why a cracked tooth hurts, it helps to know something about the anatomy of the tooth. Inside the tooth, under the white enamel and a hard layer called the dentin, is the inner soft tissue called the pulp. The pulp contains the tooth’s nerves and blood vessels.
When the outer hard tissues of the tooth are cracked, chewing can cause movement of the pieces, and the pulp can become irritated. Eventually, the pulp will become damaged to the point that it can no longer heal itself.
The tooth will not only hurt when chewing but may also become sensitive to temperature extremes. In time, a cracked tooth may begin to hurt all by itself. Extensive cracks can lead to infection of the pulp tissue, which can spread to the bone and gum surrounding the tooth.
How will my cracked tooth be treated?
There are many different types of cracked teeth. The treatment and outcome for your tooth depend on the type, location, and extent of the crack.
Craze Lines
Craze lines are tiny cracks that affect only the outer enamel. These cracks are extremely common in adult teeth. Craze lines are very shallow, cause no pain, and are of no concern beyond appearances.
Fractured Cusp

If you’ve cracked a tooth and breathing through your mouth or drinking cold fluids is painful, bite on clean, moist gauze or cloth to help relieve symptoms until reaching your dentist’s office. Never use topical oral pain medications (such as Anbesol®) or ointments, or place aspirin on the affected areas to eliminate pain symptoms.
Cracked Tooth
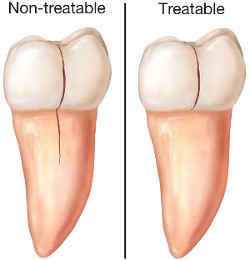 A cracked tooth means a crack extends from the chewing surface of your tooth vertically toward the root. The tooth is not yet separated into pieces, though the crack may gradually spread. Early diagnosis is important in order to save the tooth. If the crack has extended into the pulp, the tooth can be treated with a root canal procedure and a crown to protect the crack from spreading.
A cracked tooth means a crack extends from the chewing surface of your tooth vertically toward the root. The tooth is not yet separated into pieces, though the crack may gradually spread. Early diagnosis is important in order to save the tooth. If the crack has extended into the pulp, the tooth can be treated with a root canal procedure and a crown to protect the crack from spreading.
However, if the crack extends below the gum line, it is no longer treatable, and the tooth cannot be saved and will need to be extracted. That’s why early treatment is so important. A cracked tooth that is not treated will progressively worsen, eventually resulting in the loss of the tooth. Early diagnosis and treatment are essential in saving these teeth.
Split Tooth

Vertical Root Fracture

After treatment for a cracked tooth, will my tooth completely heal?
Unlike a broken bone, the fracture in a cracked tooth will not heal. In spite of treatment, some cracks may continue to progress and separate, resulting in loss of the tooth. Placement of a crown on a cracked tooth provides maximum protection but does not guarantee success in all cases.
The treatment you receive for your cracked tooth is important because it will relieve pain and reduce the likelihood that the crack will worsen. Once treated, most cracked teeth continue to function and provide years of comfortable chewing. Talk to your endodontist about your particular diagnosis and treatment recommendations.
What can I do to prevent my teeth from cracking?
While cracked teeth are not completely preventable, you can take some steps to make your teeth less susceptible to cracks.
- Don’t chew on hard objects such as ice, unpopped popcorn kernels or pens.
- Don’t clench or grind your teeth.
- If you clench or grind your teeth while you sleep, talk to your dentist about getting a retainer or other mouthguard to protect your teeth.
- Wear a mouthguard or protective mask when playing contact sports.
Reprinted with permission of the AAE. Copyright © 2018 American Association of Endodontists. All Rights Reserved.
